Everything About Customer Data: Importance, Benefits & Best Practices
Table of Contents
Every click, visit, swipe, and purchase a customer makes translates into data.
As customer interactions with businesses are rapidly evolving across social media channels, brick-and-mortar stores, and e-commerce websites, the flow of customer information increases. Results? Businesses get flooded with fragmented data, which often remains underutilized.
This data has evolved from just being a by-product of product marketing activities to being the foundation of new customer retention strategies, personalization tactics, and customer loyalty. This blog will explore what customer data is, its importance, management challenges, and the concepts around it. So without further ado, let’s begin!
What is Customer Data?
Customer data refers to any information collected about an individual’s interactions, behaviors, and preferences as they engage with any business. In essence, it’s the raw material that acts as a founding stone of a business’s lasting relationship with a customer.
Types of Customer Data
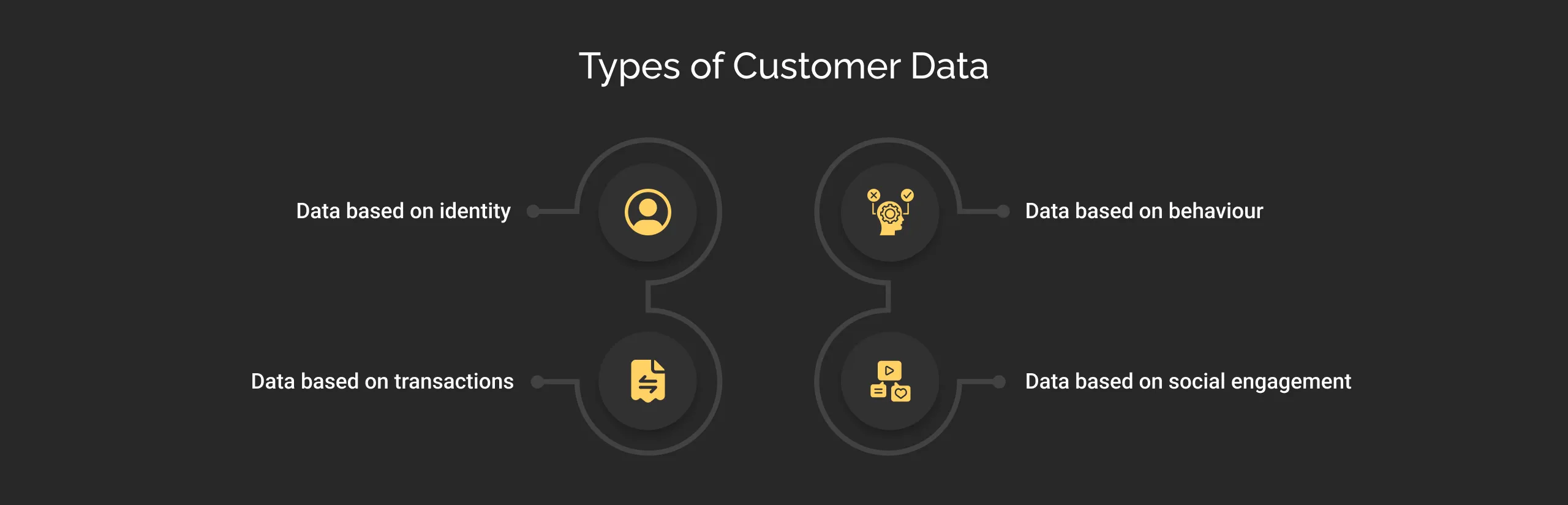
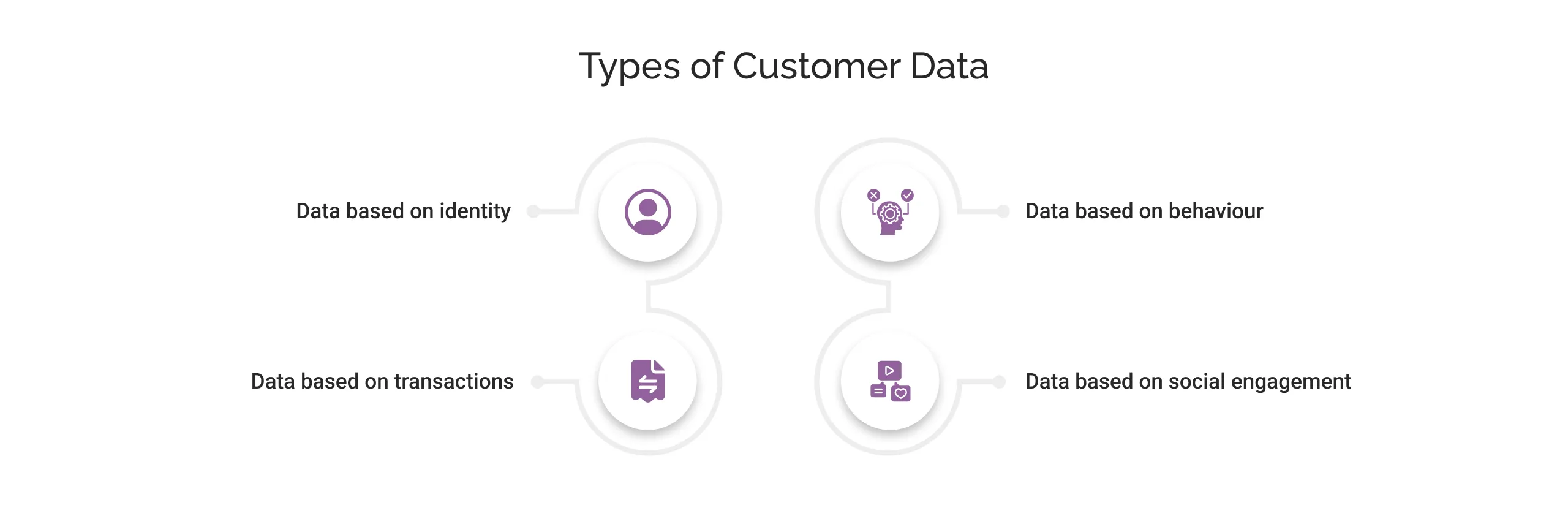
There are multiple types and aspects associated with customer data. Each type plays a specific role in understanding customers. Let us take a look at some of these types:
- Data based on identity: This is very basic yet sensitive customer data that includes their names, contact details, and gender preferences, etc.
- Data based on behaviour: This includes information like the customer’s website visits, clicks, time spent, service feedback, and engagement.
- Data based on transactions: This includes the customer’s previous transactions, payments, returns, and product usage patterns.
- Data based on social engagement: This includes the information collected across a customer’s different social media platforms.
Customer Data Glossary: Important Terms Explained

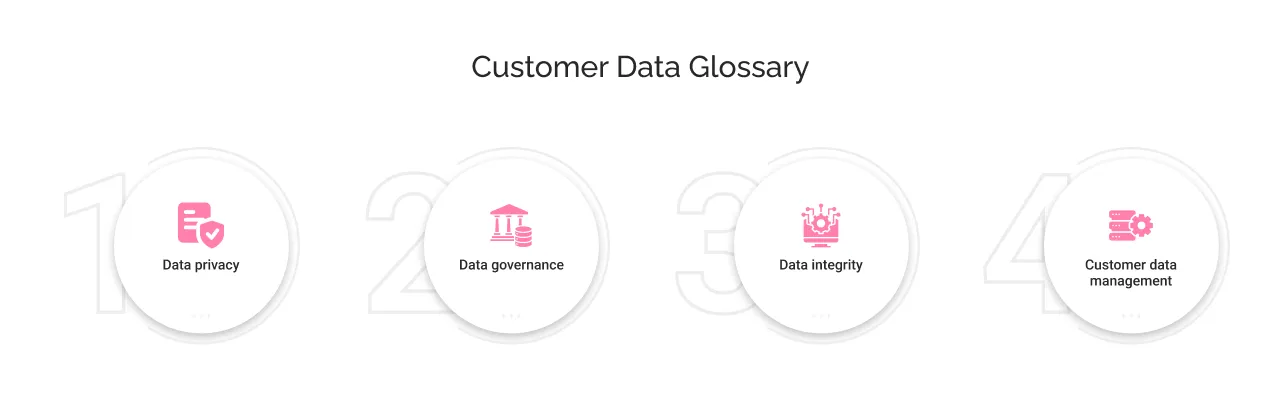
Here’s a list of some of the most important terms related to customer data that one should know before we move ahead in the blog:
- Data privacy: The concept of protecting the sensitive first-party data from misuse and breaches. It ensures that customer information is collected, stored, and used responsibly.
- Data governance: The concept of preparing frameworks and policies for safeguarding customers’ data privacy. It defines who can access data, how it’s used, and how compliance is maintained.
- Data integrity: It is the authenticity of data. Maintaining data integrity means ensuring information remains accurate, consistent, and trustworthy over time.
- Data unification: The process of integrating data from different data sources. This helps create a single, comprehensive view of the customer across platforms and touchpoints.
- Customer data management (CDM): It is the practice of organizing and maintaining customer information in one single place to ensure its accuracy and accessibility. Effective CDM supports personalized experiences and informed decision-making.
Importance of Customer Data
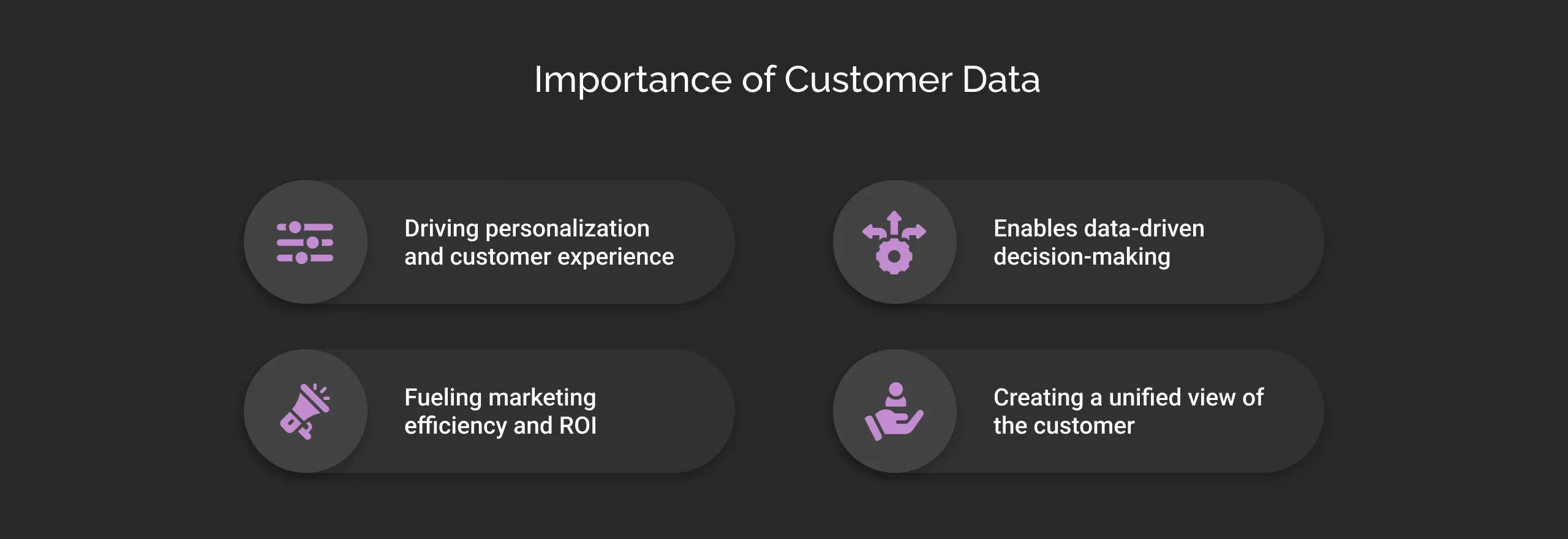
Here are the reasons that validate the importance of customer data:
Driving personalization and customer experience
Customers today expect brands to understand them beyond generic marketing. Personalized offers, product suggestions, and timely communication have become baseline expectations. Customer data enables businesses to tailor every interaction, transforming marketing from mass messaging into meaningful engagement.
Example: A financial institution can use unified customer data to recommend savings plans based on spending behavior, while a streaming platform can curate watchlists that feel intuitive to each user.
Fueling marketing efficiency and ROI
When marketing teams operate with accurate, unified customer data, every campaign becomes smarter and more cost-efficient. Data-backed segmentation ensures that the right message reaches the right person at the right time. This reduces ad waste, improves conversions, and provides a measurable lift in ROI.
Enables data-driven decision-making
Beyond marketing, customer data shapes decisions across departments. Sales teams can identify upsell opportunities, service teams can predict churn, and product teams can detect market trends early. Reliable customer data turns intuition into evidence, allowing leadership to act decisively, not reactively.
Creating a unified view of the customer
Most organizations struggle because their data is scattered across platforms: sales data in one system, marketing insights in another, and customer support tickets somewhere else. Unifying this information creates what’s often called a single customer view.
Challenges of Managing Customer Data
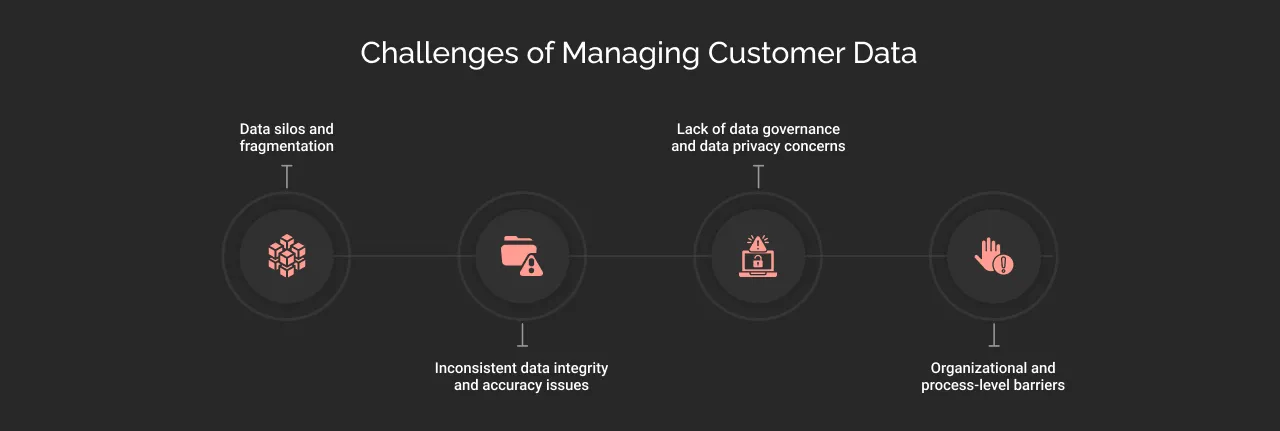
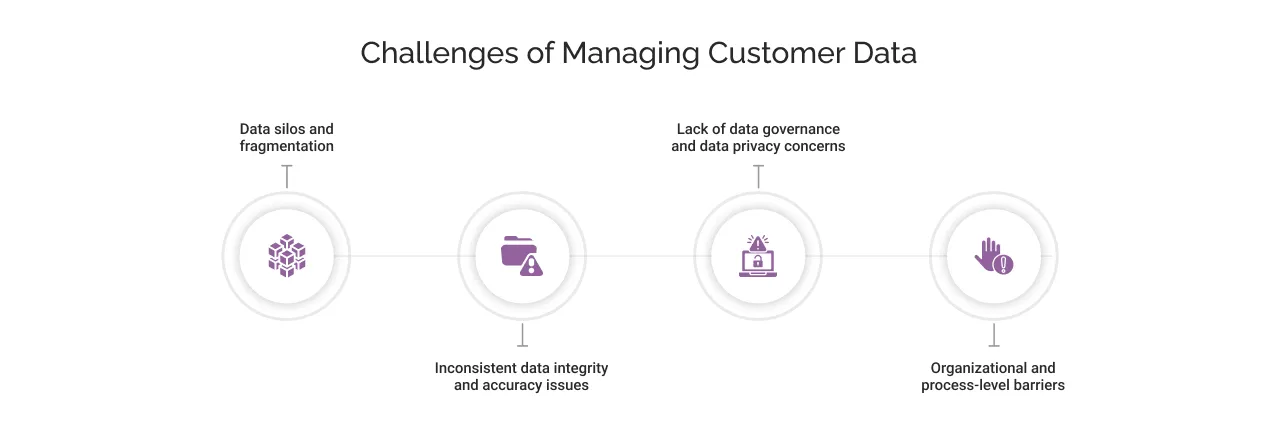
These are some of the challenges one can encounter while managing customer data:
Data silos and fragmentation
When each department maintains its own data systems, data silos are bound to form. These silos lead to increased efforts, inconsistent product messaging to the customers, and missed insights and opportunities.
Inconsistent data integrity and accuracy issues
Since customer data gets collected from various touch points, data integrity problems, such as duplicate records, incomplete fields, or outdated entries, can cause significant business inefficiencies. For example, a premium customer ends up getting a generic offer simply because the company’s data wasn’t timely updated.
Lack of data governance and data privacy concerns
Without governance, customer data can become a liability. A mature governance model is required to protect customer data against misuse, improve compliance, and build confidence among customers who are increasingly sensitive about how their information is managed. Some of the globally recognized regulations, like GDPR, CCPA, have also redefined how businesses handle customer information. Non-compliance can lead not only to penalties but also to reputation loss. Therefore, ensuring data is collected with consent, processed ethically, and stored securely is mandatory for ensuring data privacy.
Organizational and process-level barriers
Technology alone doesn’t solve data problems. Often, internal misalignment between IT, marketing, and operations creates barriers. Optimal customer data management requires collaboration, clear ownership, and a shared understanding of why data quality matters to the organization’s mission.
Best Practices to Solve Customer Data Challenges

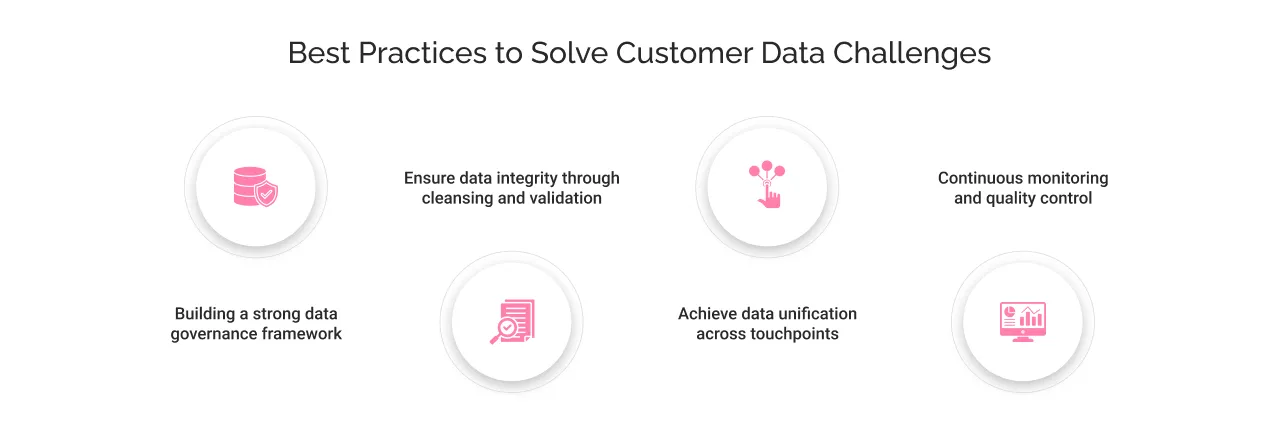
One can consider these best practices to resolve the above-discussed challenges:
Building a strong data governance framework
It’s better to be safe than sorry when it comes to dealing with sensitive customer data. Start by clearly defining the rules, protocols, and policies for data collection, access rights, and lifecycle management. This governance ensures consistency and transparency of data processing, along with preventing misuse/breach of data. Further, compliance isn’t a one-time effort. Therefore, pre-requisitely embed data privacy-by-design principles across data workflows.
Ensure data integrity through cleansing and validation
Regular audits, deduplication, and validation checks keep the customer data strategy accurate and reliable. Integrating automated quality tools helps maintain integrity even as data volumes grow.
Achieve data unification across touchpoints
Connecting systems like CRM, marketing automation, and service platforms helps create a unified customer profile. Unified data reduces redundancy and provides a 360-degree view of the customer journey, essential for modern personalization. Platforms such as Salesforce Data Cloud exemplify how data unification can be achieved at scale, connecting data from multiple sources in real time, maintaining accuracy, and ensuring it’s governed by consent.
Continuous monitoring and quality control
Customer data is dynamic; it changes as people evolve. Continuous monitoring, AI-based anomaly detection, and periodic reviews ensure that data remains current and useful. Businesses that treat data quality as an ongoing process, not a project, build a stronger foundation for long-term success.
CDP vs DMP: Understanding the Difference
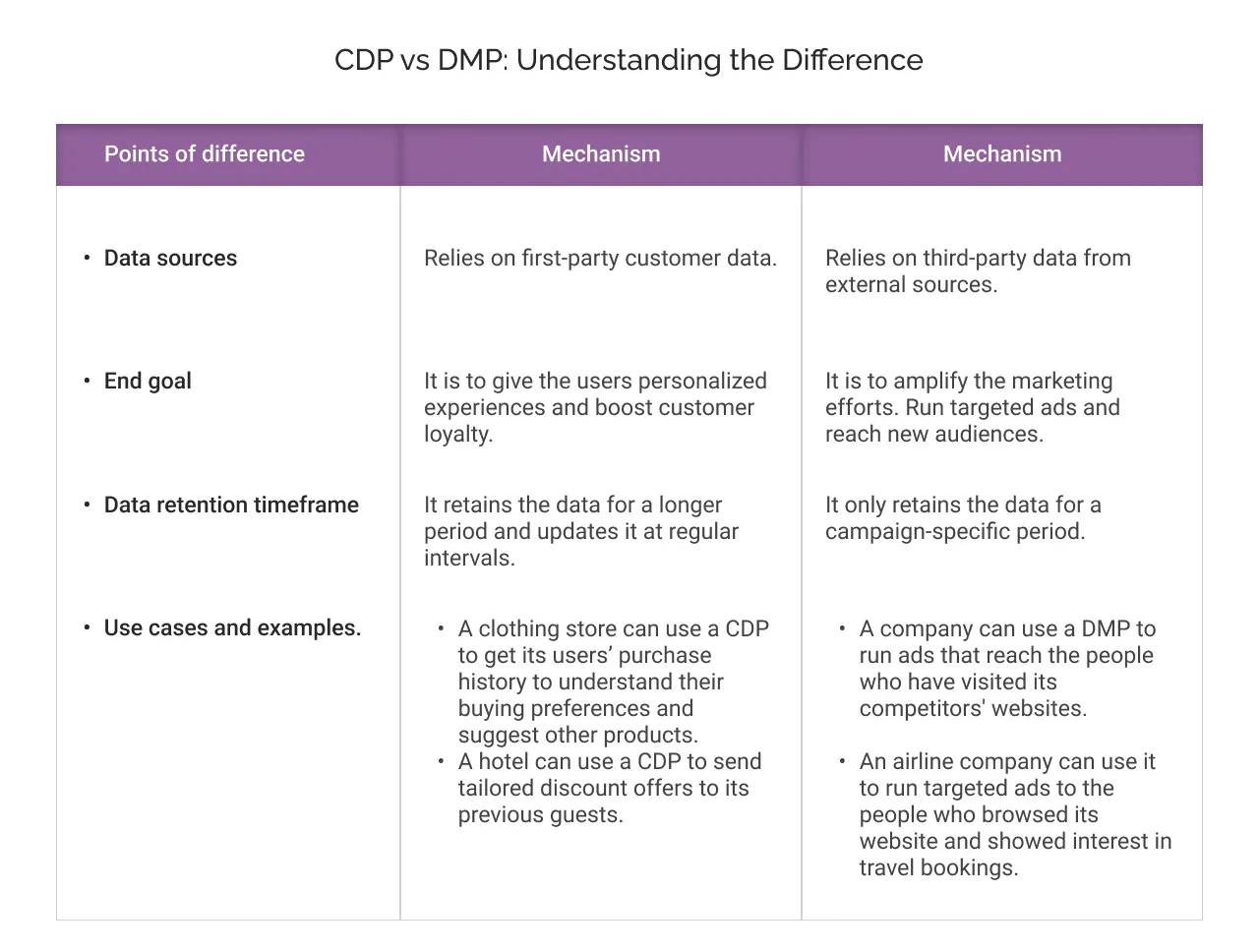
While both customer data platforms (CDP) and data management platforms (DMP) have different purposes to solve, sometimes the lines of their differentiations can get blurry. Let us understand the difference between the two:
Customer data platform:
This platform collects and unifies first-party data information that the customers willingly share through sign-ups, transactions, or loyalty programs. It then builds a unified profile of a customer from all the possible touch points, which allows for personalized recommendations in real time.
Data management platform:
This platform, on the other hand, focuses mainly on third-party data aggregated (generalized data such as demographics, etc.), anonymized information (no specifications), that can be used for running advertising campaigns.
In simpler terms:
Think of a DMP as the engine behind ad targeting on external websites, whereas a CDP helps you know your own customers better for the long-term association.
- A CDP builds relationships.
- A DMP builds reach.
Most modern enterprises rely on both, but only a CDP like Salesforce Data Cloud enables deep, consent-based insights that drive loyalty and lifetime value.

Having understood the differences between CDP vs DMP, also read about the differences between CDP vs CRM.
End Note
Customer data is no longer just a digital asset; it’s the new currency of modern business. It does it all, from powering personalizations to making informed strategies, and to effectively engaging their audiences.
To achieve this seamlessly, platforms like Salesforce Data Cloud are reliable for managing your customer data across every touchpoint.
Want to know more about how you can get started with your data activation journey? Reach out to the seasoned experts at Cyntexa now! With our Salesforce Data Cloud services, you can seamlessly elevate your CDP implementations to the next level.
Don’t Worry, We Got You Covered!
Get The Expert curated eGuide straight to your inbox and get going with the Salesforce Excellence.
AUTHOR
Vishwajeet Srivastava
Salesforce Data Cloud, AI Products, ServiceNow, Product Engineering
Co-founder and CTO at Cyntexa also known as “VJ”. With 10+ years of experience and 22+ Salesforce certifications, he’s a seasoned expert in Salesforce Data Cloud & AI Products, Product Engineering, AWS, Google Cloud Platform, ServiceNow, and Managed Services. Known for blending strategic thinking with hands-on expertise, VJ is passionate about building scalable solutions that drive innovation, operational efficiency, and enterprise-wide transformation.


Cyntexa.
Join Our Newsletter. Get Your Daily Dose Of Search Know-How