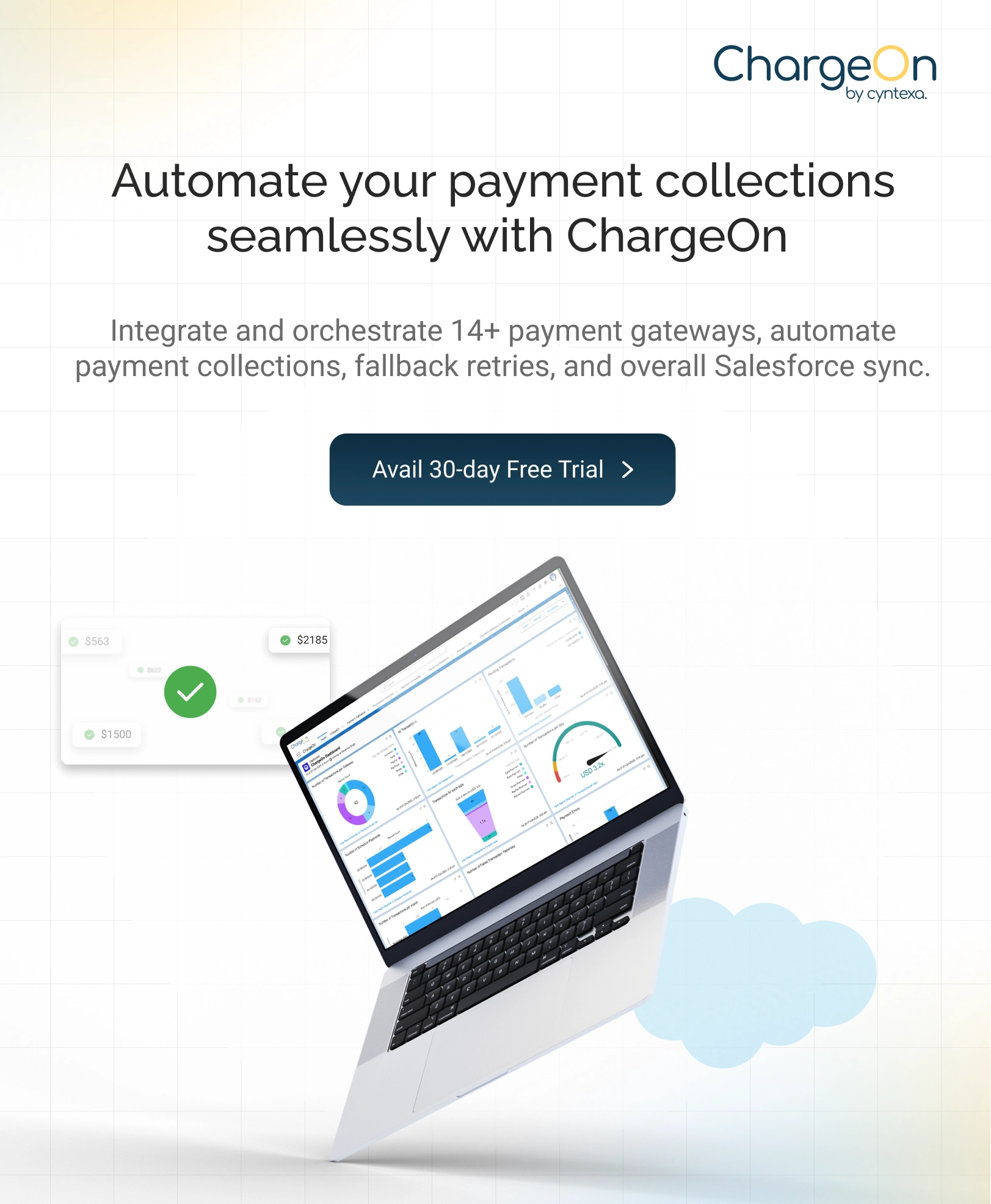
ITIL vs ITSM: Here’s the Difference
Table of Contents
Handling IT requests? Resolving incidents? That’s what ITSM (IT Service Management) is.
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is a framework of best practices for managing IT services more effectively.
Put simply, ITSM is like running an operating system, while ITIL is like operating system documentation, helping users to configure, use, and maintain the system.
So, ITIL vs ITSM is not about choosing one over the other; it’s about learning how they work together.
This blog will help you learn about the ITIL and ITSM in detail, how they work together, and the differences between them.
ITIL vs ITSM: A Detailed Understanding
What is ITIL?
ITIL is an acronym for Information Technology Infrastructure Library. As said earlier, it is a globally accepted framework for IT Service Management practices. It supports 34 ITSM practices, including incident management, change management, problem management, and service request management.
ITIL was first introduced by the UK’s Central Computing and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) in 1980. The first iteration was called Government Information Technology Infrastructure Management (GITIM), which was later renamed to ITIL in 1989. It was introduced in response to the need for a standard to make IT Services more cost-effective and value-driven by aligning them with the business objectives.
Since 1989, ITIL has evolved through multiple versions from ITIL v2 (2000), ITIL v3 (2007), ITIL 2011, to ITIL 4 (2019). ITIL 4 is the latest version as of October 2025, which introduced the concept of Service Value System (SVS). SVS connects all parts of an organization, such as guiding principles, governance, service value chain, practices, and continual improvement.
Today, ITIL is used by organizations across 180+ countries to improve service delivery and align IT with business goals.
What is ITSM?
ITSM, or IT Service Management, refers to the practice of designing, developing, managing, and optimizing IT services to align with business goals and users’ needs.
ITSM was introduced in 1989 with the introduction of the ITIL framework. ITIL set the foundation for ITSM by providing codified best practices to improve IT services, focusing on the user needs.
Some of the core ITSM processes include incident management, problem management, service request management, and more.
ITIL vs ITSM: How do they work together
Here in this section, we will discuss how ITIL improves the core ITSM processes. This will help you understand the importance of this integration:
1. Incident management
Let’s consider a scenario where an application has crashed, and nearly half of the organization’s employees are affected, impacting their operations. It is a must for the IT team to restore the services immediately to ensure minimal impact on business operations.
Now, let’s see how ITIL, when applied, will standardize the process:
- Identification and logging: The incident will be logged in the ITSM system automatically with information such as affected systems, timestamp, and potential issues
- Prioritization: Based on the severity of the incident, ITIL will assign P1 priority to the incident (high impact and high urgency)
- Investigation: The IT team follows the ITIL’s structured approach, which includes searching for the Known Error Database (KEDB) for similar past incidents. The KFDB has information related to documented problems with proven solutions or workarounds. For example, they might find out that such incidents occurred earlier as well due to a memory leak with a workaround that restored the services. The subsequent steps would be followed to restore services
- Restoration: A workaround is implemented based on ITIL’s resolution hierarchy (temporary fix now, permanent solution later)
- Closing: The incident will be marked closed with root cause analysis, resolution steps, and time metrics per ITIL requirements.
In this case, ITSM defined the work that is restoring the services, while ITIL defined the essential steps to ensure the issue is resolved promptly.
2. Change management
Let’s consider a scenario when an organization is in need of upgrading its database. Here is how ITIL-aligned ITSM can help:
- Change request creation: Following ITIL’s change model, the request includes business justification, risk assessment, rollback plan, and affected services
- Change assessment: ITIL’s change authority model determines who approves (standard, normal, or emergency change)
- Change Advisory Board (CAB): For significant changes, ITIL prescribes a CAB review examining impact, timing, and resource requirements
- Implementation planning: ITIL’s approach requires detailed schedules, communication plans, and success criteria
- Post-implementation review: ITIL mandates reviewing whether the change achieved objectives and lessons learned
The database upgrade (ITSM work) follows ITIL’s structured change control process, reducing failed changes, minimizing disruption, and ensuring organizational learning.
These are the two examples of how ITIL aligns the ITSM with the business needs.
ITIL vs ITSM: What are the differences?
1. Definition
As said, ITIL is a documented collection of best practices, processes, and guidance. While ITSM is a practice focused on delivering and managing IT services.
2. Scope and limitations
The scope of the ITIL is defined and specific to each version. For example, ITIL 4 supports around 34 practices categorized into general management, service management, and technical management.
ITSM has no certain limitations. It can work either by following ITIL guidelines or without ITIL guidelines. Beyond ITIL, ITSM also exists following the other guidelines, including Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF), custom methodologies, or informal practices.
3. Flexibility
ITIL guidelines are structured and adaptable within the guidelines. It emphasizes following specific processes or guidelines that are specific to flows, roles, and activities. For example, ITIL’s incident management process follows specific processes (detection, logging, categorization, prioritization, diagnosis, resolution, closure).
ITSM is a highly adaptable practice. Organizations can customize the ITSM processes to meet their specific needs beyond the ITIL guidelines. Additionally, organizations also have the flexibility to use ITSM tools such as ServiceNow ITSM with adaptable workflows to meet specific organizational needs and be driven by the ITIL guidelines.
4. Governance
ITIL was launched and governed by the UK’s Central Computing and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA). As of 2025, it is managed by PeopleCert. It is a global certification organization that holds ITIL’s intellectual property and trademark rights.
Simply said, ITIL is a guideline that is centrally managed by a single entity that has control over the following:
- Official ITIL publications and updates
- Certification schemes and examination content
- Licensed training providers and accreditation
- Use of ITIL trademarks and branding
- Framework evolution and version releases
ITSM capabilities are offered by multiple companies. For example, ServiceNow has its own ITSM; similarly, BMC Helix has Remedy. Put simply, ITSM is not governed by a single entity; the control and management are subject to the tool you choose.
ITIL-based ITSM tools
Here we have compiled a list of some of the ITSM tools driven by the ITIL guidelines:
1. ServiceNow ITSM
As the name suggests, ServiceNow, an AI-powered cloud-based platform, offers ITSM capabilities. ServiceNow ITSM is built on the ITIL-4 guidelines, helping organizations with a unified approach to manage IT incidents, problems, change, service requests, configuration management, and more. It is trusted by some of the world’s leading organizations, including Coca-Cola.
2. BMC Helix ITSM
Helix ITSM is a cloud-based ITSM service management platform enabling organizations to automate, orchestrate, and optimize core ITSM processes. These processes include, but are not limited to, incident, problem, and change management.
BMC Helix ITSM is built on the ITIL-4 guidelines and used by organizations such as SAP, CGI, A1 Telekom Austria Group, and more.
Read also: ServiceNow vs. Remedy (BCM Helix ITSM): Choosing the Right ITSM Solution. This blog will help you understand which ITSM tool aligns with your organization’s needs.
3. Jira Service Management
Introduced by Atlassian, Jira Service Management helps organizations to centralize their ticketing for incidents, changes, requests, and problems. It is built on the ITIL guidelines and used by organizations such as ENGIE Mexico, Nextiva, Rockwell Automation, CBS, Saint-Gobain, and more.
Read also: Jira vs ServiceNow: Which One to Choose? This blog will help you understand the difference between these two ITSM tools, helping you to choose the best one aligned with your organizational needs.


Final take
Both ITIL and ITSM have their own importance and coexist to help organizations align IT services with their specific objectives.
We at Cyntexa hold official partnerships with leading ITSM providers like ServiceNow & Salesforce and can help you assess your current processes, select the right ITSM platform, and implement a solution that drives operational excellence.
Schedule a consultation call today!
Don’t Worry, We Got You Covered!
Get The Expert curated eGuide straight to your inbox and get going with the Salesforce Excellence.
AUTHOR
Shruti
ServiceNow, Sales Cloud
Shruti is a ServiceNow Consultant with 5+ years of experience across ServiceNow ITSM, AWS, Salesforce Loyalty Management, and managed services. She blends technical expertise with strategic insights to deliver transformative IT services and CRM solutions that enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction.


Cyntexa.
Join Our Newsletter. Get Your Daily Dose Of Search Know-How