Why Trust Salesforce with Your Data? Inside the World’s #1 CRM Security Framework
Table of Contents
Salesforce is the world’s #1 CRM, trusted by businesses of all sizes from startups to large enterprises, to collect, organize, and manage their customer data efficiently.
Startups to Fortune 500 companies like Amazon, Microsoft, Coca-Cola, and Mercedes-Benz Group rely on Salesforce not just for its CRM capabilities but also for its unwavering commitment to protecting sensitive business and customer data.
For businesses using Salesforce, data security is crucial as it stores a vast amount of sensitive data, including financial records, customer information, and sales data. All of these make this platform vulnerable to cyberattacks.
A single instance of a data breach might result in not only financial loss, but also deterioration in customers’ trust.
Fortunately, Salesforce is continuously evolving its robust security measures to safeguard data. But how exactly does it work, and what can you do to strengthen your org’s security?
This blog will break down how Salesforce protects your data and best practices for data security. But firstly, let’s understand what is data security in Salesforce.
What is Data Security in Salesforce?
Salesforce has a multi-layer data security model that includes tools, policies, and practices, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of information. It only allows authorized people to access, modify, and share the sensitive information within the organization.
Salesforce Data Security Model
Salesforce’s data security model secures data through a multi-layer security model, ensuring data is protected at every level to minimize risk. This model works as a defense in depth model- multiple layers of security instead of one – that combines authentication, authorization, and encryption.

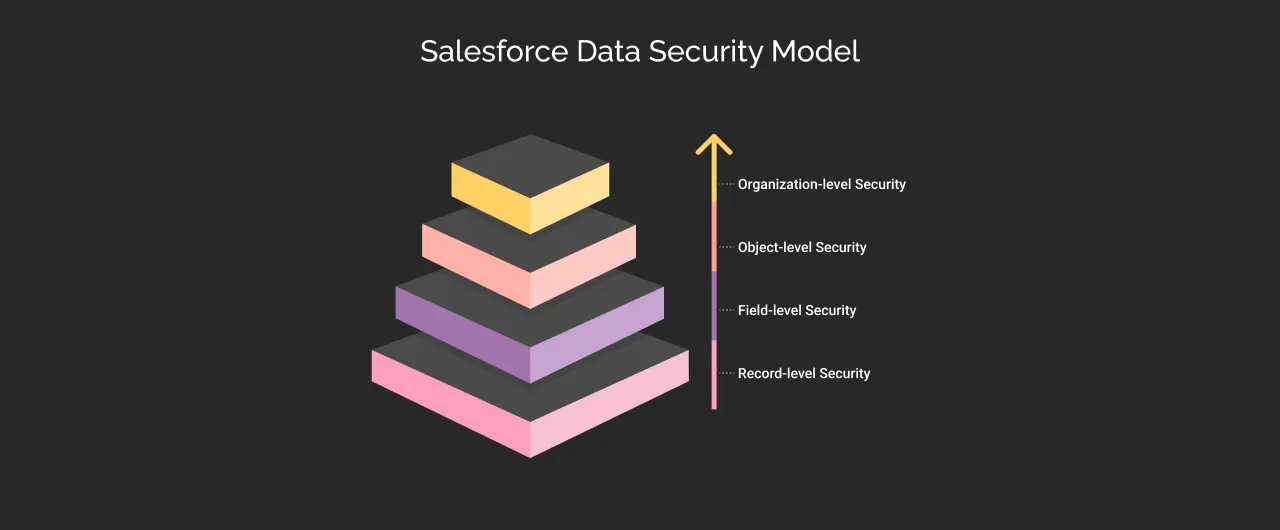
Here’s how it works.
Organization-level Security
Salesforce allows you to set the foundational rules for who can access Salesforce org and under what conditions (like limiting logins to certain hours and locations). It helps to maintain a list of authorized users and create strong password policies.
For example, setting MFA (Multi-factor Authentication) and IP restrictions, preventing account takeovers, and reducing phishing risks. While it provides robust cloud security, it’s important to remember that cybersecurity is a shared responsibility. Tools like Bitdefender, Norton, and Kaspersky protect devices and networks from malware, phishing, and ransomware attacks, complementing Salesforce’s cloud protections. Together, these measures form a layered defense that helps keep sensitive business and customer data safe.
Object-level Security
Object-level data security enables you to set permissions on a specific type of object to prevent a group of users from creating, editing, viewing, or deleting any record of that object. Simply put, admins can control which types of data users can see or edit and limit overexposure of sensitive data.
For example, an HR team can access payroll data but can not access sales pipelines.
Field-level Security
Field-level security allows you to restrict access to specific fields even if someone has access to the object.
For example, a support agent can see a customer’s name but not their payment information (such as credit card numbers).
Record-level Security
Record-level security determines who can access or edit individual records in your Salesforce org, like ensuring sales reps can only view accounts they own, not the entire customer database. You can manage record-level access in four ways:
- Organization Wide Defaults (OWD)
Sets the default access level for all accounts in your org as Private, Public Read-Only, or Public Read/Write.
For example, if OWD for opportunities is set to private, sales reps cannot see each other’s deals unless granted access.
- Role Hierarchy
Role hierarchy grants higher-level users automatic access to records owned by their team members or those below them in the hierarchy.
In simple words, a regional Sales VP can access all opportunities owned by their reps (team members), but reps can not see their VP’s records.
- Sharing Rules
Sharing rules automatically grant access to records to specific groups even if OWD is private.
For example, A customer support group gets read-only access to all Cases, even if OWD restricts them.
- Manual Sharing
Manual sharing allows a record owner/ admin to temporarily share a particular record with another user. This gives flexibility without compromising security long term.
For example, a sales rep can share a key opportunity with a product specialist for a customer demo.
In summary, Salesforce’s data security model works on providing least privilege to employees (only see what they need), reducing insider risks and human errors while ensuring compliance (audit trails show who accessed what).
Key Features of Salesforce Data Security

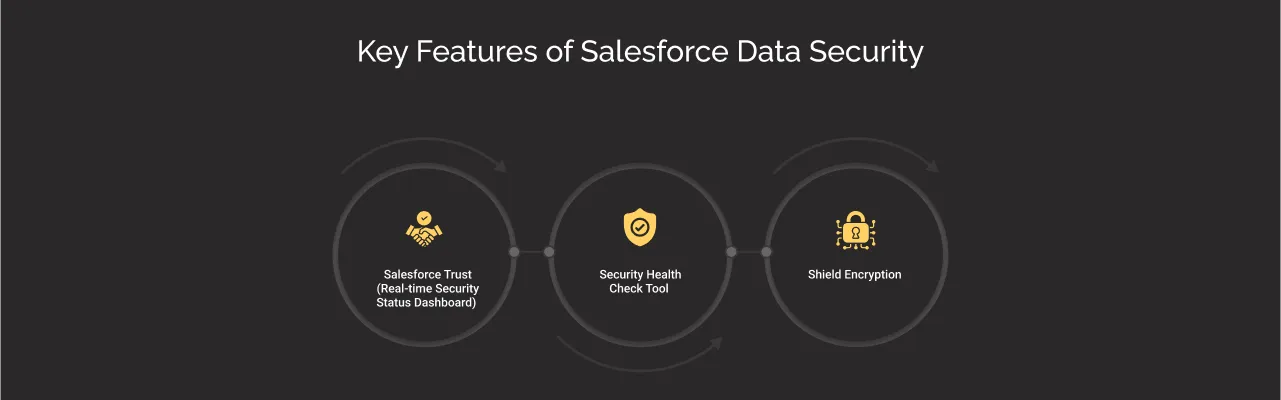
Salesforce offers built-in security tools to help businesses protect their sensitive data proactively. Here is a breakdown of its critical features, how they work, and why they matter.
1. Salesforce Trust (Real-time Security Status Dashboard)
It provides live updates on Salesforce’s system performance, security incidents, and maintenance. It also shows historical data on past outages and breaches, and you can see if Salesforce experiences a global issue first. You can identify if the problem is on the Salesforce end or your end.
How to Use Salesforce Trust?
- Visit www.trust.salesforce.com
- Check the specific product section for real-time status. For example, if there is an outage or other issue, the dashboard will display 1 or more incidents.
2. Security Health Check Tool
Salesforce Health Check tool scans your Salesforce org for misconfigurations (such as overly permissive sharing rules and weak passwords). This provides a view of security posture scores (0-100%) and suggests fixes as well.
How to Use Salesforce Security Health Check?
- Go to setup -> Health Check
- Review the risk level marked as (Critical/high/medium/low).
- Click on “Fix Risks” to apply recommended fixes.
3. Shield Encryption
Salesforce Shield encryption helps you protect your data by encrypting it with keys that can be managed efficiently. It uses key derivation and direct encryption to protect the data. It ensures you meet strict compliance (HIPAA, GDPR) for sensitive data.
How to Enable Salesforce Shield Encryption?
- Go to Setup (from the quick find box)
- Search for Encryption
- Then, Shield Platform Encryption Settings
5 Best Practices for Strengthening Salesforce Security
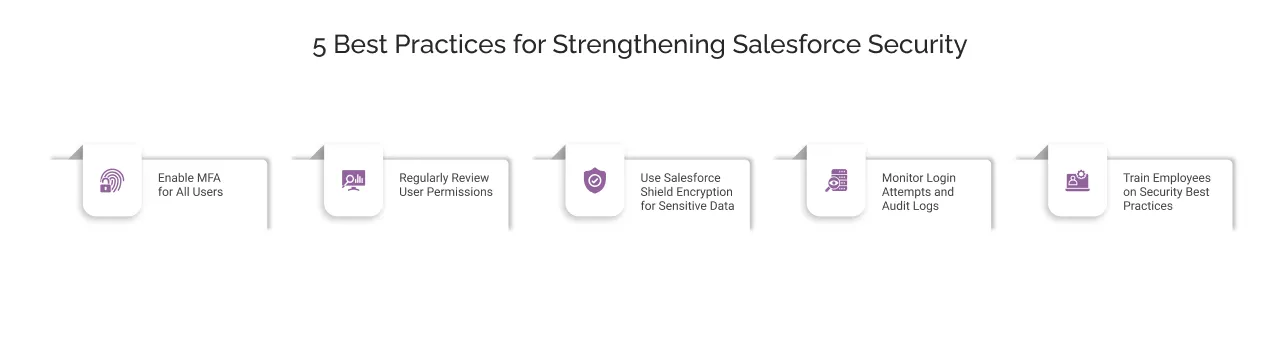

Salesforce provides a wide range of data security tools, but how you configure them determines how well your data is protected. Here are the Salesforce security best practices to safeguard your data effectively.
1. Enable MFA for All Users
As cyberattacks are increasing daily, protecting your Salesforce org with only a password is not sufficient. It can be easily compromised through phishing attacks, leaks, and brute-force attacks. To ensure robust Salesforce cybersecurity, you can:
- Enable MFA for all internal users in your Salesforce org (Setup-> Quick Find Box-> Enter Identity -> Select Identity Verification-> Select Require Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
Example: A financial services firm enabled MFA and reduced account phishing and data leaks.
2. Regularly Review User Permissions
Over-provisioned access is a top cause of data breaches, such as unnecessary permissions to ex-employees. 74% of data breaches happen due to human elements like people involved either via error, privilege misuse, and use of stolen credentials, according to Verizon’s data breach investigation report.
To eliminate the risks related to unnecessary permissions, you can:
- Execute quarterly audits for “User Permissions and Sets” to ensure who can access the sensitive data and objects, such as contracts and payment records.
- Enforce the Salesforce health check tool to identify overly permissive settings.
- Utilizing the least privilege principle means providing users with the required permissions only.
Example: A healthcare provider discovered 50+ inactive users with access to patient data during a regular audit.
3. Use Salesforce Shield Encryption for Sensitive Data
Salesforce Shield uses two methods, Database Encryption and Field-Level Encryption, to protect sensitive data. Both paths encrypt a broader range of data than standard encryption. To implement shield encryption, you can:
- Identify critical fields and use data classification to tag fields needing encryption.
Note: Shield encryption fields can not be used in reports or filters, so plan workflows accordingly.
Example: An e-commerce company encrypted bank account details using Shield Encryption, ensuring only authorized users/teams can decrypt them.
4. Monitor Login Attempts and Audit Logs
Suspicious logins, such as midnight access from unauthorized users and from another country, and unauthorized data exports (Bulk record downloads) often precede leaks. So, monitoring login attempts and audit logs is essential to eliminate such breaches. You can set up alerts through:
- Failed logins (Setup-> Login History-> Create Alert)
- Data exports (Setup-> Data Export-> Monitor “Export Data” logs)
- Use Event Monitoring to track API calls from unknown IPs.
Example: A retailer detected an employee exporting customer emails and other personal details to a personal account via audit logs, preventing the data breach.
5. Train Employees on Security Best Practices
As we discussed earlier, more than 70% of breaches take place due to human errors. Training employees on data security and management becomes essential, so they can leverage the power of data and AI features of Salesforce. You can provide them with quarterly security training on:
- Spotting phishing emails.
- Secure sharing practices such as never setting Reports to “Public Read” permissions.
- Simulated phishing tests (help them be aware of and how to respond in such situations).
- Train developers to revoke unused integrations and restrict OAuth scopes.
Example: After training on Salesforce data protection, a sales team stopped clicking phishing links, reducing breaches.
Bonus Tips
- Limit logging to corporate IPs through (Setup -> Network Access)
- Enforce re-login for users after more than 15 minutes of inactivity.
- Block sensitive data from being shared externally.

Conclusion
Salesforce data privacy is not like setting up and forgetting; it is about proactive monitoring, least privilege access, and employee training. These are the differentiators between a secure Salesforce org and the headline of a breached org.
If you want to strengthen security, our Data and AI experts can help you strengthen your Salesforce org’s security and help you leverage the full potential of data.
Don’t Worry, We Got You Covered!
Get The Expert curated eGuide straight to your inbox and get going with the Salesforce Excellence.
AUTHOR
Vishwajeet Srivastava
Salesforce Data Cloud, AI Products, ServiceNow, Product Engineering
Co-founder and CTO at Cyntexa also known as “VJ”. With 10+ years of experience and 22+ Salesforce certifications, he’s a seasoned expert in Salesforce Data Cloud & AI Products, Product Engineering, AWS, Google Cloud Platform, ServiceNow, and Managed Services. Known for blending strategic thinking with hands-on expertise, VJ is passionate about building scalable solutions that drive innovation, operational efficiency, and enterprise-wide transformation.


Cyntexa.
Join Our Newsletter. Get Your Daily Dose Of Search Know-How
Frequently Asked Questions
Data Security refers to the set of best practices, policies, and tools used to protect digital information from unauthorized access. It involves safeguarding data from various threats like cyber attacks, accidental data loss, and data breaches.
A data breach can cost millions of dollars and ruin customer trust. The average cost of a data breach in 2024 reached $4.88 million, a 10% increase from the previous year (IBM Data Breach Cost Report). Over 500 million Facebook records were exposed in 2019, highlighting the risks of poor data protection and reputational damage.