What Is Salesforce Implementation? Strategies and How to Implement
Table of Contents
Salesforce has changed the way businesses interact with their customers. It manages extensive customer data in one place, changing the scenario of customer interaction management. However, implementing the platform effectively requires proper planning and technical expertise.
Many businesses try to implement Salesforce on their own without understanding the complexities involved, leading to inferior results.
In this blog, you will learn about Salesforce implementation, its benefits, challenges, different phases, strategies, and why you need a partner for your Salesforce implementation. Everything in this blog will guide you through the process to successfully implement Salesforce and leverage its capabilities.
What is Salesforce implementation?
Salesforce implementation is a process of configuring the CRM (Customer Relationship Management) platform according to your business requirements, including customizing objects, fields, layouts, workflows, etc.
This process centralizes all business interactions and enables businesses to improve customer relationships through real-time customer data and informed strategies. It involves several steps: planning, customizing, data migration, and integrating CRM with other tools.
For example, a business selling men’s apparel online manages its customer data in spreadsheets and a separate marketing tool. With the increasing number of customers, they recognize the need for a robust system to manage sales and marketing.
With the consulting services, they decided to implement Salesforce Sales Cloud and integrate the platform with the existing marketing tool. They can track customer orders, manage leads, and send targeted email campaigns.
What Are the Key Phases of Salesforce Implementation?
A Salesforce implementation is most effective when it follows a clear, phased structure. Each phase serves a specific purpose: reducing risk, aligning teams, and ensuring that the platform delivers measurable business benefits. Instead of treating Salesforce as a one-time deployment, leading organizations approach implementations as a lifecycle that gives them strategy, execution, and scope for continuous improvement in one go.
Below are the key phases that define a well-executed Salesforce implementation.
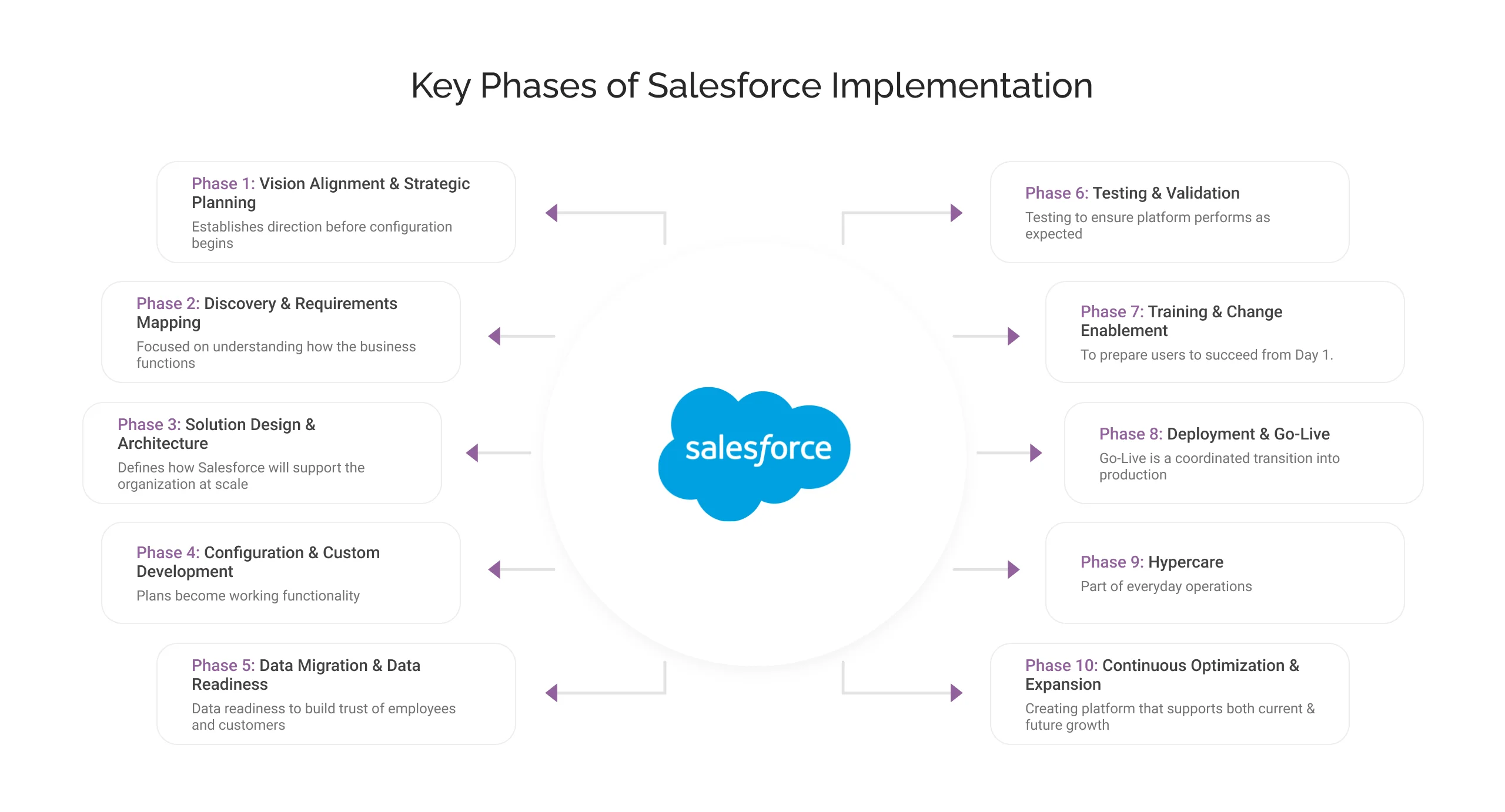
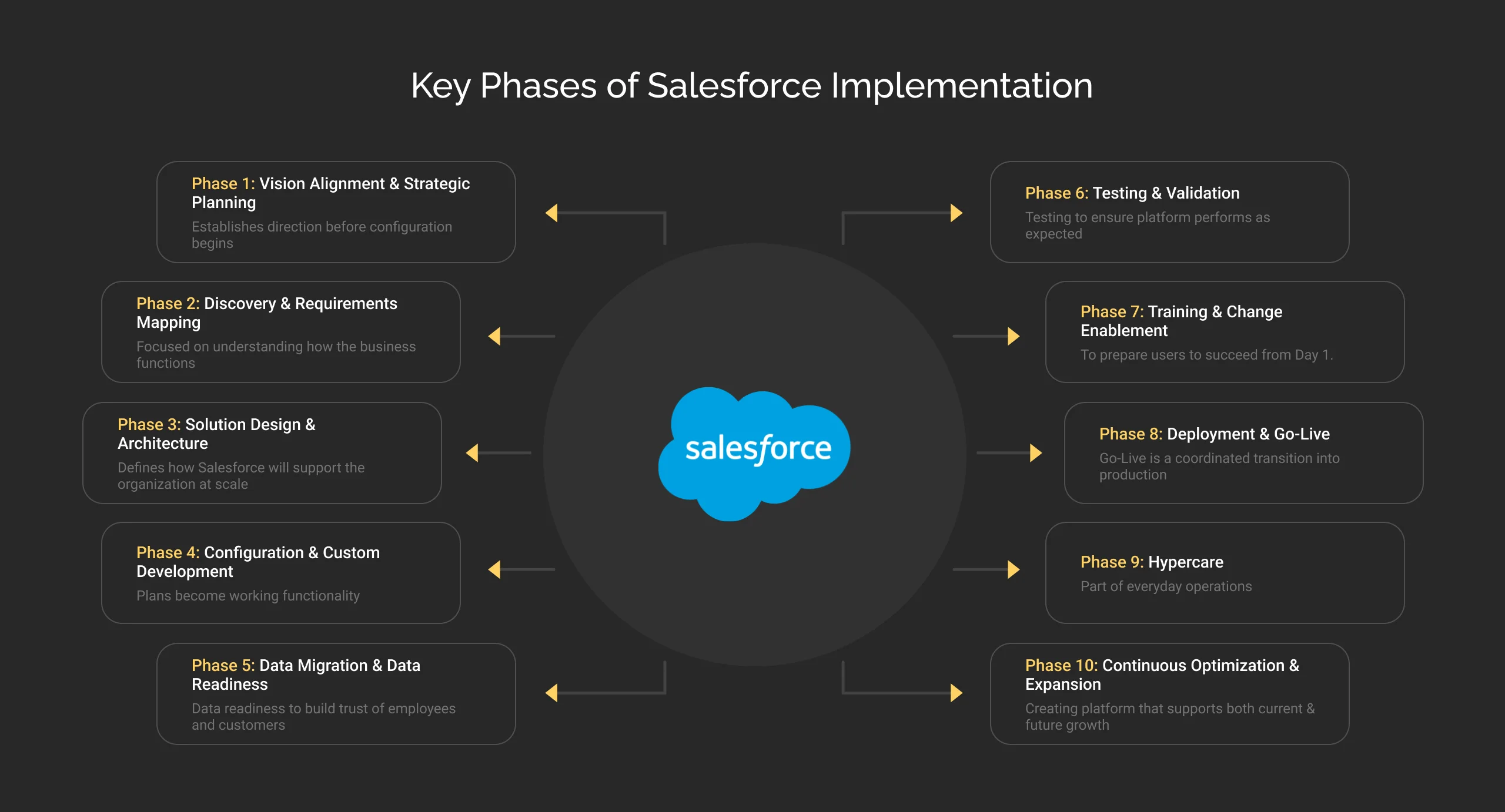
Phase 1: Vision Alignment & Strategic Planning
This is the first phase that establishes direction before configuration begins.
Align teams on the agenda, why Salesforce is being implemented, which business problems it is expected to solve, and the perimeter for measuring success. Executive sponsorship, decision-making authority, and governance models are discussed transparently to avoid delays later in the Salesforce implementation process. Scope boundaries are intentionally defined so teams understand what will be delivered now vs. in future phases.
Careful planning ensures Salesforce will support business priorities rather than becoming a collection of disconnected features.
Phase 2: Discovery & Requirements Mapping
Discovery is the next stage that is focused on understanding how the business functions.
Workflows are reviewed across teams to identify inefficiencies, dependencies, and exceptions. Data sources are assessed for quality, ownership, and relevance. Before moving ahead in finalizing the Salesforce CRM architecture and workflows, gather requirements from finance, marketing, operations, or external platforms.
The outcome of this phase is a prioritized, validated set of requirements grounded in real processes, not assumptions. Strong discovery brings alignment between business teams and the Salesforce implementation partner before design begins.
Phase 3: Solution Design & Architecture
The third phase of Salesforce implementation defines how Salesforce will support the organization at scale.
Salesforce architects design the data model, security framework, automation strategy, and integration approach. Decisions are made around standardization versus flexibility, keeping in mind that teams can work efficiently while maintaining consistency. Reporting and analytics requirements are built into the design so insights are available from day one.
When designed with Salesforce implementation best practices, the architecture delivers consistent performance, scalability, and adaptability as business needs evolve.
Phase 4: Configuration & Custom Development
In this phase, plans become working functionality.
Salesforce is configured using standard capabilities wherever possible: objects, fields, flows, validation rules, and Lightning experiences. Automation is designed to guide users without adding unnecessary complexity. Many companies also go ahead with custom Salesforce development if there is a requirement.
Development is shared in different sprints/ milestones, allowing teams to review and share feedback (if the development needs any changes).
Phase 5: Data Migration & Data Readiness
Data readiness is one of the key indicators that builds the trust of both employees and customers in a platform.
Make sure you are getting your legacy data reviewed, cleaned, and de-duplicated, and mapped carefully to Salesforce. Teams decide which historical data is meaningful to bring forward and which should remain archived. Multiple migration cycles are often used to test accuracy and check results before final cutover.
Clean, reliable data at launch creates a high rate of user adoption and confidence in Salesforce reporting.
Phase 6: Testing & Validation
Testing ensures Salesforce performs as expected in real-world scenarios.
Functional testing confirms that configurations and automations work correctly. Integration testing checks the data flow between connected systems. User Acceptance Testing (UAT) allows business users to validate end-to-end workflows by implementing real use cases.
This phase provides confidence that Salesforce is assisting all the connected teams in their day-to-day operations and highlights changes before going live.
Phase 7: Training & Change Enablement
Training prepares users to succeed from day one.
When you work with a seasoned partner offering Salesforce implementation services, they will ensure that your team gets role-based training on how Salesforce supports specific responsibilities, rather than generic features overviews. Supporting materials such as quick guides and in-app prompts also help in learning.
Change enablement also helps teams understand why processes are changing and how Salesforce fits into their routine work. You can ensure the strongest adoption by making your team feel supported, informed, and confident.
Phase 8: Deployment & Go-Live
Go-Live is a coordinated transition into production.
Final data loads are completed, integrations are activated, and access controls are verified. Cutover plans include monitoring and contingency steps to address issues quickly. Support teams are available to assist as and when required during the initial rollout.
A smooth go-live reflects preparation across all earlier phases.
Phase 9: Hypercare
Most of the implementation service providers offer Hypercare post Salesforce implementation. In the weeks following launch, teams respond to questions, resolve issues and improve configurations based on the real user experience. Adoption metrics and feedback suggest small adjustments that improve usability and performance.
This phase helps Salesforce become part of everyday operations rather than a parallel system.
Phase 10: Continuous Optimization & Expansion
Salesforce will grow with your business. Teams review performance metrics, user feedback, and business priorities to identify enhancements. New automation, reports, integrations, or advanced capabilities can be built when the requirement arises. Continuous optimization ensures Salesforce remains aligned with changing goals and growth. This phase turns Salesforce into a long-term platform for innovation and improvement.
Each phase of a Salesforce implementation plays a clear role in driving adoption and value. When executed with discipline, these phases come together to create a platform that supports both current needs and future growth.
Different Approaches for Salesforce Implementation
There are various Salesforce deployment strategies that come with their benefits and drawbacks. Knowing about all the approaches helps to make the best choice depending on your requirements.
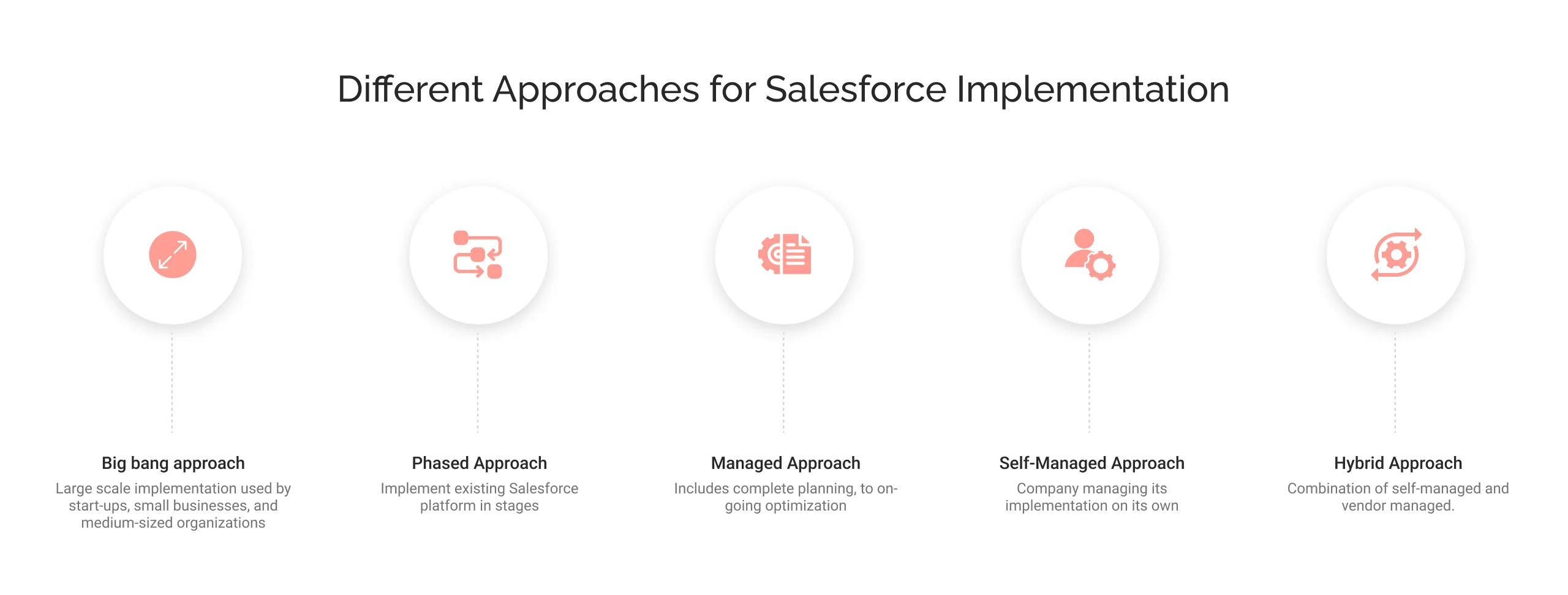
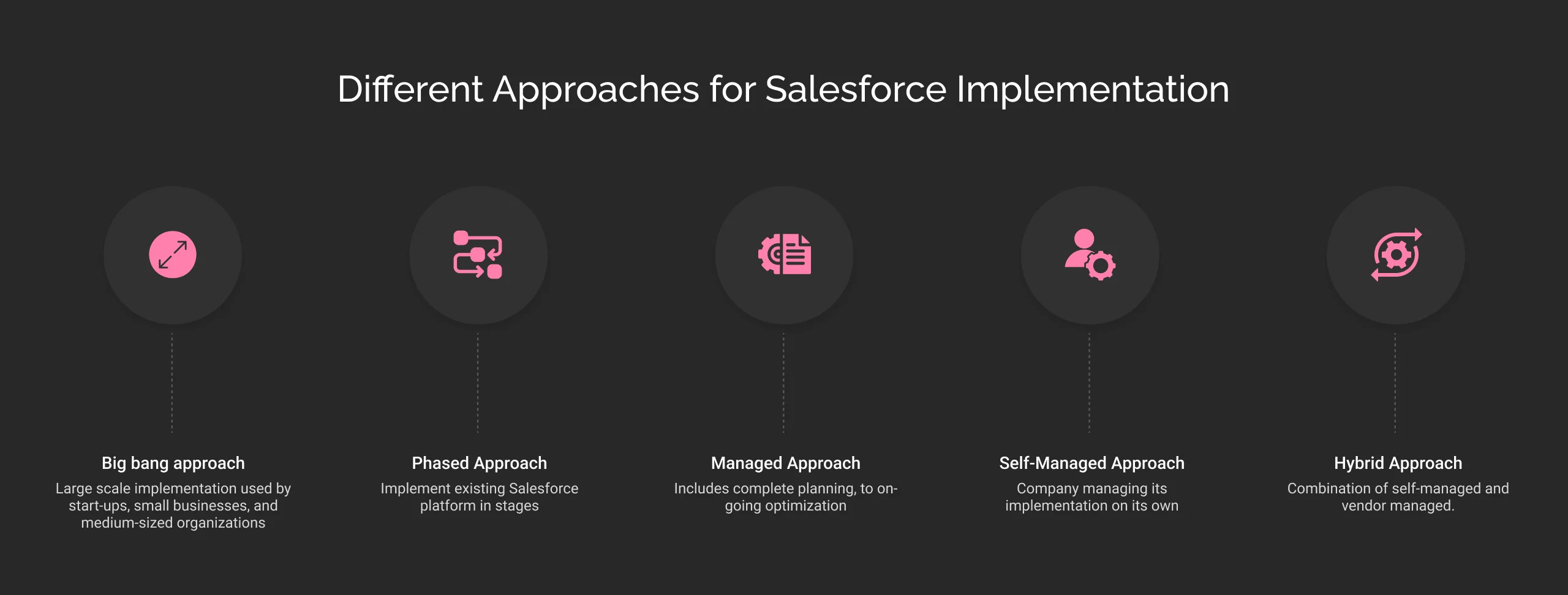
1. Big Bang Approach
The Big Bang strategy is a large-scale implementation that consolidates the existing system and processes into a single process. Start-ups, small businesses, and medium-sized organizations often use this approach. If you have any questions about how Salesforce can help small businesses, refer to the guide.
Benefits: The Big Bang approach is useful for those organizations that want to move all users to the Salesforce platform. Also, it is cheaper and faster than other approaches. It can provide a higher return on investment (ROI) as all resources are focused on change management at the same time.
Drawbacks: The Big Bang approach involves high risk, and overlooking a small detail can cause big issues for all users. It requires more planning as rollback might not be possible after final implementation.
2. Phased Approach
The phased approach or strategy enables businesses to implement the existing Salesforce platform in stages. It includes various stages and is helpful for larger enterprises that want to gradually shift to a new platform.
Benefits: It minimizes risk as testing is easier for single stages and helps teams gain more knowledge with each stage to improve implementation and configuration.
Drawbacks: It can be expensive in the long run and time-consuming for organizations.
3. Managed Approach
In the managed approach, the implementation partner takes full responsibility for the project. Whether it is planning, Salesforce customization, configuration, data migration, user training, or going live.
Benefits: Taking a managed approach enables you to get in-depth expertise from implementation specialists. It reduces risks and complexities, leading to a faster process.
Drawbacks: Relying only on the implementation partner can limit your flexibility, and businesses may feel less control over the process.
4. Self-Managed Approach
In the self-managed approach, it is the sole responsibility of the organization to manage the implementation with its resources and technical expertise.
Benefits: It provides businesses with full control over the implementation and results. This can be cost-effective and enhance your internal expertise and customization.
Drawbacks: Requires significant technical expertise and resources to complete the full process. This is a time-consuming process for the org, and a lack of specialization leads to delays and implementation issues.
Refer to this guide to understand how much it costs to implement Salesforce.
5. Hybrid Approach
The hybrid approach is a combination of managed and self-managed strategies. In this, vendors are responsible for specific phases of implementation, and businesses manage to do some phases on their own.
Benefits: The hybrid approach allows businesses to leverage the technical expertise of implementation while utilizing team knowledge over specific aspects of the projects. It can be more cost-effective than a fully managed strategy and allows companies to take technical expertise where they lack.
Drawbacks: Miscommunication between the partner and business can lead to potential implementation complications.
These are the key Salesforce implementation strategies that businesses can choose according to their need to leverage the full potential of CRM.
Top 7 Salesforce Implementation Strategies
Salesforce implementations succeed not because phases are followed, but because the right strategic decisions guide how those phases are executed and sustained over time, whether it’s a first rollout or a reimplementation.
Here we have shortlisted the top 7 Salesforce Implementation strategies that leading companies are using:
1. Salesforce Must Be the Single Source of Operational Truth
The most important and early decision in any Salesforce implementation is whether the platform replaces existing ways of working or will operate alongside them. In successful implementations, Salesforce becomes the primary system of record. Legacy CRMs are restricted, spreadsheets lose their credibility, and reports outside Salesforce are no longer a source of truth.
This shift can be uncomfortable, as it requires change before full value is visible. However, without this enforcement, Salesforce remains optional, and optional systems are rarely trusted or adopted consistently.
2. Implementation Scope Must Be Defined by One Clear Business Priority
Strong Salesforce architecture must define scope around a specific, unresolved business challenge rather than a list of platform capabilities. This challenge may relate to forecasting accuracy, customer visibility, process handoffs, or leadership oversight.
Evaluate all the features in the initial release based on whether they directly address the tension or not. Eliminate features that aren’t helping at all, even if they are easy to implement. This discipline ensures early value and keeps expansion aligned with business priorities.
3. System Design Must Reflect Real Working Practices
Salesforce implementations are stuck when systems are designed around idealized processes instead of actual working practices. Effective design starts by acknowledging how teams operate today, including exceptions and informal workflows.
Introduce automation gradually to support and guide behavior rather than enforce it in the early stages. When users see their reality reflected in the system, adoption improves.
4. Data Quality Must be Owned By the Business
Many organizations treat data quality as a migration task. Mature Salesforce implementations treat it as a business responsibility. Before data is cleansed or migrated, ownership and accountability for each data domain must be clearly defined.
This approach maintains data quality after go-live, not just during implementation. Trust in Salesforce reporting depends on ongoing accountability, not one-time cleanup efforts.
5. Customization Must be Justified by Clear Business Value
Customization is unavoidable in successful implementation, but it is applied with discipline. Every deviation from standard Salesforce behavior must have a clear and defensible business reason.
This approach keeps the platform easier to manage, safer to upgrade (when required in the future), and understandable over time. It also reduces dependency on original builders and supports confident platform evolution.
6. Go-Live Must Establish Ongoing Accountability
In high-performing organizations, go-live is considered the beginning, not the end, of operational accountability. Key decision-makers are using Salesforce data actively in reviews and decision-making. Data gaps and usage issues are addressed as leadership actively uses Salesforce data in reviews and decision-making. Data gaps and usage issues are addressed openly.
When Salesforce is visibly used by leadership, it becomes operationally relevant. Adoption at this stage is driven by expectation, not encouragement.
7. Salesforce Must Be Built to Adapt as the Business Changes
Salesforce should be designed with the expectation of change. Flexible and scalable design choices allow the platform to support growth and new requirements without frequent rework, ensuring long-term value and stability.
Implementations do not fail due to missing features, but due to unclear direction. These strategies bring early structure and accountability, enabling Salesforce to function as an operational foundation.
Common Salesforce Implementation Challenges And How Partners Solve Them
Every Salesforce implementation encounters challenges. What sets successful implementations apart is not the absence of issues, but how early those issues are identified and addressed. Implementation partners help in turning those challenges into opportunities for alignment, adoption, and long-term value on the Salesforce.
Below are the most common challenges organizations face, along with how partners typically help resolve them.
1. Unclear Business Objectives and Misaligned Expectations
Many Salesforce projects begin with broad goals but limited clarity. When objectives are framed in general terms like improving visibility or modernizing CRM, teams struggle to make consistent decisions during design and build. This often results in expanding scope, competing priorities, and difficulty demonstrating value after go-live.
How partners help:
Salesforce implementation partners bring clarity and structure to early planning discussions. They work with leadership and business teams to convert high-level goals into measurable outcomes. By defining success criteria clearly and aligning stakeholders with them, partners help keep the implementation focused on outcomes rather than features.
2. Poor Data Quality and Complex Data Migration
Data challenges are among the most common issues in Salesforce implementation. Customer data is often spread across multiple systems, outdated, duplicated, or inconsistently maintained. Migrating this data without proper preparation can quickly put Salesforce in a bad spot.
How partners help:
The right implementation partner treats data as a business asset, not just a technical task. They assess data sources early, establish data ownership, and guide data cleansing as well as deduplication before migration begins. Through iterative migration and validation, partners help ensure Salesforce launches with data that users can rely on. You can refer to this blog for the top Salesforce implementation partner for your business.
3. Difficulty integrating Salesforce with existing systems
Salesforce mostly works around multiple apps and systems. Integrating it with ERP, finance, marketing, or support systems introduces complexity related to data timing, consistency and ownership. Poorly planned integrations can disrupt operations and create conflicting information.
How partners help:
Salesforce partners bring architectural expertise to integration design. The experts lookout where real-time data is required versus scheduled updates, recommend appropriate integration patterns, and implement monitoring to maintain reliable data flows. This allows Salesforce to function as a connected platform rather than a single system.
4. Low user adoption and resistance to change
Sometimes, well-designed Salesforce solutions can also face problems when users fail to adopt new ways of working. Resistance often comes from limited involvement, unclear benefits, or workflows that feel disconnected from daily responsibilities.
How partners help:
Partners work actively on change enablement throughout the implementation, not just at the end. They involve users early, design role-based experiences, and support training focused on real tasks. Clear communication around the purpose and value of Salesforce helps get more engagement from users.
5. Over-Customization and Growing Technical Debt
Salesforce’s flexibility makes customization easy, but excessive or poorly justified customization can increase complexity, maintenance effort, and upgrade risk. This typically occurs when short-term needs outweigh long-term platform considerations.
How partners help:
Implementation partners apply design discipline by encouraging standard Salesforce capabilities wherever possible. They ensure customizations are tied to clear business needs and supported by governance and architectural reviews. This helps organizations maintain flexibility while protecting platform stability.
These challenges are not signs of poor planning; they are part of almost every Salesforce journey. What matters is having the right expertise in place to address them early and consistently.
Signs You Need a Salesforce Implementation Partner
A lot of businesses feel the need to hire a Salesforce implementation partner only after they face some issues. These issues are not always technical. In most cases, they are operational, with unclear ownership of data or access, and sometimes growing complexity that internal teams struggle to manage alone.
Here are some signs that can help you evaluate whether you need an implementation partner or not.
1. When Teams Disagree on Core Definitions and Handoffs
A common issue occurs when sales, marketing, and service teams do not share the same definitions for leads, opportunities, stages, or handoffs. These differences often come up during Salesforce implementation and quickly slow progress.
If you have chosen a partner from the top Salesforce implementation partners, help align teams on shared definitions and design workflows that remove confusion and mismanagement. The alignment helps in making Salesforce a single source of truth.
2. When Integrations Work Initially but Break Over Time
Many integrations look fine in the early days, but start falling apart when the data grows. This typically happens when integrations are built only for current needs, and not planned for future scalability needs.
Partners plan for growth and design integration patterns that remain reliable in the long term. This prevents recurring issues that internal teams often discover too late.
3. When Security and Access Rules are Unclear or Inconsistent
Security gaps come into notice only after users gain access to Salesforce. Improper permissions, unclear role access, and compliance concerns can invite serious risk.
Implementation experts work on strengthening security models early, ensuring access is aligned with roles and responsibilities. This reduces exposure and avoids reactive fixes later.
4. When Salesforce Usage Levels Off After Early Adoption
It is common for Salesforce usage to slow down after initial excitement fades. Users may log in less frequently or revert to old tools if Salesforce does not clearly support their work.
Salesforce experts address adoption as an ongoing effort. They help align Salesforce usage with daily tasks and reinforce its role beyond launch.
5. When Industry-Specific Knowledge Is Required
Many businesses operate in regulated or specialized industries. In these cases, generic Salesforce configurations are often insufficient.
Partners with industry experience understand common requirements, compliance needs, and data structures. This reduces trial-and-error and accelerates implementation quality.
6. When Multiple Salesforce Clouds Are Involved
Implementations that span Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, Marketing Cloud, CPQ, or Data Cloud introduce added complexity. Coordination across clouds requires architectural planning and governance.
Partners help ensure different clouds work together in a consistent and scalable way.
If Salesforce is business-critical and mistakes would be difficult to reverse, external expertise is often the safer choice.
Engaging a Salesforce implementation partner is not about capability; it is about context. The more Salesforce influences coordination, accountability, and decision-making, the more value a partner can provide.
Final Words
Salesforce helps businesses in multiple ways, from centralizing customer information to increasing sales, better data management, enhanced collaboration, flexibility, growth adaptation, and more. However, leveraging these lucrative benefits can only be possible when you coherently plan before Salesforce implementation.
Even if you are unsure about doing the process on your own and do not have technical expertise, don’t worry. Our all-around experts at Cyntexa can help you throughout the process from planning to execution. Our Salesforce-certified specialists will ensure a successful Salesforce implementation that matches your business objectives so you can acquire the desired results.
Don’t Worry, We Got You Covered!
Get The Expert curated eGuide straight to your inbox and get going with the Salesforce Excellence.
AUTHOR
Shubham
Service Cloud, Salesforce Managed Packages
With over 5 years of experience, Shubham specialize in curating solutions on Salesforce Service Cloud, Nonprofit Cloud, Consumer Goods Cloud, Managed Packages, and ServiceNow ITSM. He designs and implements end-to-end service solutions that improve operational workflows and ensure seamless integration across enterprise systems. Shubham’s expertise lies in creating secure, efficient, and agile platforms tailored to unique business needs.


Cyntexa.
Join Our Newsletter. Get Your Daily Dose Of Search Know-How